The Ross Sea in Antarctica is one of the last places in the ocean that remains untouched by human life. This makes it very special. It has a rich and different environment with species that are not found anywhere else such as unique fish, penguins, and whales. The environment here is still clean, meaning it is free from pollution and overfishing, which is rare in today’s world.

Studying the Ross Sea helps scientists understand how climate change is affecting polar regions. Since it is so untouched it serves as a baseline for comparison with other more impacted areas. As we move into 2024, the Ross Sea is getting a lot of attention because it’s a key part of efforts to protect marine life and keep our planet’s environment healthy.
Its maintenance is important not just for maintaining its own unique environment, but also for learning how to better protect other parts of our oceans.
Table of Contents
Geographical view of the Ross Sea
The Ross Sea, situated in the Southern Ocean, spans about 600,000 square miles. This expanse makes it a substantial portion of Antarctic waters.
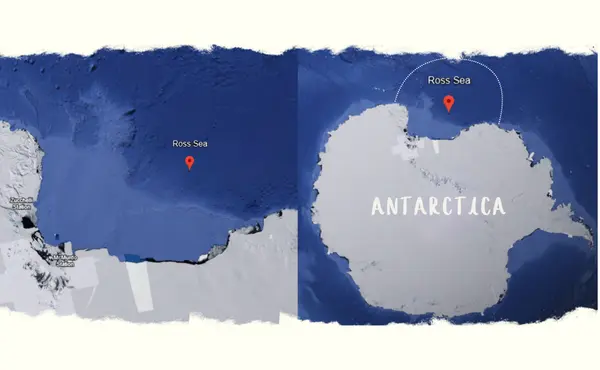
It lies to the south of New Zealand and is bordered by the Ross Ice Shelf to the south and Victoria Land to the west. The region’s harsh yet majestic surroundings attract adventurers and researchers alike.
Key Features of the Ross Sea
The Ross Ice Shelf, the world’s largest floating ice platform, dominates the southern boundary. It’s not the only attraction; Mount Erebus, an active volcano, towers with its perennial snow.
Additionally, several islands, such as Beaufort Island and Ross Island, provide habitats for various Antarctic wildlife. These features not only define the geographic landscape but also support diverse ecological communities.
The Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is one of the largest ice shelves in the world. It’s like a giant floating platform made of ice, where the land meets the sea.
This shelf is constantly changing, with chunks of ice breaking off and drifting away. It’s fascinating to think how the ice shelf plays a vital role in climate studies, giving scientists insight into the effects of global warming.
The Rich Ecosystem
The Ross Sea is not just about ice and water; it’s teeming with life! It’s home to various species, including seals, penguins, and a multitude of fish.
The nutrient-rich waters here create a perfect playground for these animals. The region even hosts one of the most significant populations of Emperor penguins. Picture them waddling across the ice—it’s a sight like no other!
Climate and Weather Patterns
The Ross Sea experiences a polar climate with long, dark winters and short, intensely bright summers. Seasonal variations significantly affect marine life, with ice cover persisting through the colder months and retreating during summer.
These climatic conditions shape the rich biodiversity and influence everything from migration patterns to breeding cycles.
Biodiversity in the Ross Sea
Often termed the “Last Ocean,” the Ross Sea serves as a sanctuary for myriad species and a repository of Earth’s evolutionary history.
Marine Fauna
The marine life here is nothing short of extraordinary. The region supports a complex food web, with krill forming the basis of many species’ diets.
Seals, whales, and fish species flourish, contributing to a vibrant and balanced ecosystem. This diversity underscores the Ross Sea’s global ecological importance, as highlighted by scientific research.
Conservation Efforts
In recent years, the Ross Sea has benefited from robust conservation efforts. In 2016, the area was designated a Marine Protected Area (MPA), safeguarding it from commercial fishing for 35 years.
This initiative, detailed by NOAA, balances environmental protection with sustainable use, aiming to preserve its pristine environment.
Geopolitical Significance in 2024
The Ross Sea holds not only ecological but also geopolitical weight. As global warming alters ice patterns, this inaccessible region becomes a potential site for resource exploration and shipping routes.
International Treaties and Agreements
Key international agreements, such as the Antarctic Treaty System, govern activities in the Ross Sea, advocating for peace and cooperation.
Their relevance in 2024 is more critical than ever as nations grapple with territorial claims and environmental responsibilities in this dynamic region.
Scientific Research and Collaboration
Collaboration among scientists is crucial in the Ross Sea. Research efforts from around the world focus on studying climate change effects and marine biology, promoting international cooperation. These scientific endeavors underline the need for shared stewardship and understanding of Antarctic ecosystems.
Impact of Climate Change
The Ross Sea is not immune to climate’s transforming hand. Rising temperatures and changing ice conditions signal shifts in ecological stability.
Effects on Marine Life
Warming waters and ice melt can drastically alter habitats for marine species. The Ross Sea’s residents, from plankton to larger predators, face new challenges as climate change induces alterations in their environment. Detailed analysis is available through research like this study.
Future Projections
Looking ahead, the future of the Ross Sea is entwined with broader global environmental trends. If current conditions persist, profound changes in biodiversity and marine productivity are likely.
These scenarios, explored in various scientific publications, emphasize the need for vigilance and proactive conservation strategies.
Conclusion
The Ross Sea stands as a testament to the delicate balance of our planet’s ecosystems. Its significance in 2024 encompasses ecological health, scientific research, and international diplomacy. Protecting this region isn’t just an environmental issue—it’s a global imperative that demands collaboration and sustained commitment.
As we cast our gaze into the future, the Ross Sea remains both a symbol of Earth’s resilience and a reminder of the urgent challenges we face in preserving our natural world.

